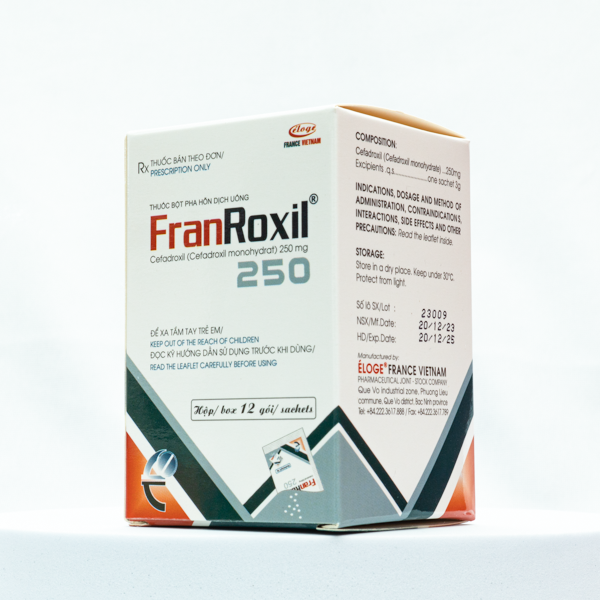
Description
Prescription drugs
Read the instructions carefully before use
Keep out of reach of children
Inform your doctor or pharmacist about any side affects you may experience when using the medicine
INGREDIENTS:
Active ingredients:
Cefadroxil (in format of Cefadroxil monohydrat) ……………… 250 mg
Excipients: White sugar, saccharin, peach smell just one a pack.
DOSAGE FORMS:
Package contains white powder, homogeneous fragrance.
INDICATIONS:
Cefadroxil is used to treat infections caused by susceptible bacteria:
- Sore throat, tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus
- Uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
- Skin and soft tissue infections.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION:
Usage: Dilute with a little water. It should be taken with food to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Dose: Take the medicine as directed by your doctor. The usual dose is as follows:
Adults and teenagers > 40 kg:
- Sore throat, tonsillitis due to Streptococcus: 1g / day (4 packs per day), take once or twice in 10 days.
- Uncomplicated urinary tract infections: 1-2 g / day (4-8 packs / day), take once or twice.
- Skin and soft tissue infections: 1g / day (4 packs per day), take once or twice
Children (< 40kg):
- Sore throat, tonsillitis due to Streptococcus: 30 mg/kg/ day, take once or twice in 10 days.
- Uncomplicated urinary tract infections: 30 mg/kg/ day, take twice.
- Skin and soft tissue infections: 30 mg/kg/ day, take once or twice.
Elderly: Cefadroxil renal excretion, kidney function test and dose adjustment as in patients with renal failure.
Renal impairment: For patients with renal impairment, adjust the dose according to the creatinine clearance as follows:
| Creatinine clearance level | Starting dose | Maintenance dose |
| 0 – 10 ml/minute/1,73 m2 | 1000 mg | 500 mg, every 36 hours |
| 10 – 25 ml/minute/1,73 m2 | 1000 mg | 500 mg, every 24 hours |
| 25 – 50 ml /minute/1,73 m2 | 1000 mg | 500 mg, every 12 hours |
Hemodialysis patients receive one additional dose of 500-1000 mg at the end of treatment.
Cefadroxil is not indicated for the children with renal impairment and hemodialysis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Hypersensitivity to cefadroxil, cephalosporin antibiotics, or any component of the drug.
- History of severe allergic reactions to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics.
WARNING AND PRECAUTIONS WHEN USING MEDICINE:
- Be cautious with asthmatics or severe allergic reactions
- For patients with a history of mild hypersensitivity reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics (non-cephalosporin group), caution should be exercised when cefadroxil is used as cross allergies may occur.
- If there is an allergic reaction (urticarial, rash, pruritus, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory disorders, syncope), the drug should be discontinued immediately and appropriate management measures (sympathetic, corticosteroid, antihistamine).
- For patients with renal failure, caution should be exercised and dosage adjusted. Before and during treatment, clinical monitoring and appropriate laboratory testing are needed.
- During long-term use of cefadroxil, it is advised to regularly test the blood formula and liver function tests.
- Long-term use of cefadroxil may cause overgrowth of non-susceptible strains. Care should be monitored carefully, if the infection is over, stop using the drug.
- There have been reports of pseudomembranous colitis with broad-spectrum antibiotics, so attention should be given to this diagnosis in patients with severe diarrhea associated with the use of antibiotics. Caution should be exercised when prescribing for people with gastrointestinal disease, especially colitis.
- Use caution in infants and premature infants.
- Effects on test results: During and after treatment with cefadroxil, Coombs positive test results may be obtained. This also occurs when Coombs is performed in infants born to mothers treated with cephalosporin prior to delivery. Anti-copper glucose test (Benedict’s solution, Fehling’s solution, Clinic test) can give false positive results. Glucose oxidase should be used.
- Patients with rare genetic conditions such as fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption, sucrase-isomaltase deficiency should not be used because of sugar-containing drugs.
Each pack contains 2.75g sugar. In diabetic patients, if the daily dose in excess of 5g / day, the daily sugar intake should be included
THE PREGNANT AND BREAST FEEDERS:
- There have been no reports of adverse effects on the fetus, but due to lack of adequate studies on the use of cefadroxil in pregnant women, caution should be exercised only during pregnancy, where necessary.
- Cefadroxil is excreted in breast milk with low concentration, but caution should be used when breastfeeding, so it is important to occur diarrhea and rash.
EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON THE DRIVERS AND MACHINE OPERATORS:
It can cause headaches, dizziness, tension, sleeplessness and fatigue, which can affect the ability to drive and operate machines.
INTERACTION, INCOMPATIBILITY:
- Do not use cefadroxil with bacteriostatic (tetracycline, erythromycin, sulfonamide, chloramphenicol) as it will cause adverse effects.
- Avoid using cefadroxil with aminoglycoside antibiotics, polymyxin B, colistin, high dose diuretics, due to possible synergism with renal toxicity.
- Regular coagulation tests should be performed when cefadroxil is used concurrently with anticoagulants, platelet aggregation inhibitors to prevent hemorrhagic complications.
- Probenecid can reduce the secretion of cefadroxil, leading to increased serum concentrations of drugs and bile.
- Cefadroxil is associated with cholestyramine which may reduce the bioavailability of cefadroxil.
UNWANTED EFFECTS:
Common, 1/100 ≤ ADR < 1/10
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, tongue inflammation.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: itching, rash, urticaria.
Rare, 1/1000 ≤ ADR < 1/100
Infections: The development of opportunistic microorganisms (fungi) such as vaginal yeast infections, candidiasis.
Rare, 1/10 000 ≤ ADR < 1/1000
Blood and lymphatic system: Increased eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, neutropenia, granulocytopenia (rare condition of prolonged drug use, return to normal when discontinued)
Immune: serum-like response
Hepatic: liver failure, cholestatic liver failure, lightly increase in transaminase (ASAT, ALAT) and alkaline phosphatase.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: angioedema
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue: joint pain
Renal – Urinary: interstitial nephritis.
Other: fever
Very rare, ADR < 1/10 000
Blood and lymphatic system: autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Immune: allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)
Neurology: headache, insomnia, dizziness, tension
Gastrointestinal: pseudomembranous colitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: Stevens Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme
Other: tired
OVERDOSE AND TREATMENT
Symptoms: Based on experience with other cephalosporins, overdose of cefadroxil can cause the following symptoms: nausea, hallucinations, spontaneous hyperreflexia, pyelonephritis, drowsiness, coma, kidney failure.
Treatment: Constipation or gastric emptying, hemodialysis if needed. Control and regulate water balance, electrolytes, kidney function control.
PHARMACOLOGY PROPERTIES
Pharmacological group: 1st generation cephalosporin antibiotic. ATC code: J01DB05.
Cefadroxil is an oral antibiotic, the first-generation cephalosporin. The drug kills bacteria by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cells by binding to one or more penicillin-binding proteins. As a result, the bacterial cell wall is less stable with osmotic pressure and the bacteria are lysed.
Mechanism of drug resistance:
– Cefadroxil is inactivated by beta-lactamase that can hydrolyze cephalosporins, such as broad-spectrum beta-lactamases and cephalosporinases produced by genes encoding chromosomes, such as the AmpC enzyme.
– Change in penicillin-binding proteins, reducing their affinity with beta-lactam.
– Reduced permeability of bacterial cells.
– Pumping antibiotics out of cells.
Relationship between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics:
Percentage versus dose interval that the drug concentration in the non-binding form remained above the minimum inhibitory concentration (% T> MIC) was the most important pharmacokinetic – pharmacodynamic the in vivo efficacy of cephalosporins.
Performance spectrum:
– Sensitive bacteria include:
Gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Groups B, C, G, Streptococcus pyogenes
– Resistant bacteria can be acquired:
Gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus (susceptible to methicillin), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae
Gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Citrobacter diversus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Proteus mirabilis
– Resistant bacteria:
Gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Enterococci, Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin resistance), Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin resistance), Streptococcus pneumoniae (intermediate and penicillin resistance)
Gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Acinetobacter spp., Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., Morganella morganii, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, Providencia stuartii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis
Other strains: Chlamydia spp., Mykoplasma spp., Legionella spp.
PHARMACEUTICAL PROPERTIES
Cefadroxil is stable in acid and is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Feed did not affect plasma absorption and peak plasma concentrations. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within 1-2 hours and range from 10 to 18 mcg / ml after 500mg and 24 to 35mcg / ml after single dose administration.
About 20% of cefadroxil is bound to plasma proteins. Cefadroxil is widely distributed in tissues and body fluids. The average volume of distribution is 18 liters / 1.73 m2, or 0.31 liters / kg. Cefadroxil passes through the placenta and excreted in breast milk.
The drug is not metabolized. More than 90% of the dose excreted in the urine is constant in the past 24 hours by glomerular filtration and renal tubular secretion. Cefadroxil is largely eliminated through artificial kidney dialysis. The plasma half-life of the drug is about 1.5 hours in people with normal renal function, lasting 20 to 24 hours in patients with renal failure. Cefadroxil is excreted through hemodialysis.
In patients with renal impairment, due to cefadroxil elimination is slow so it is necessary to increase the distance between the doses
PACKING SPECIFICATIONS:
Box of 12 packets x 3g; Box of 10 packs x 3g
STORAGE CONDITIONS:
In dry places, the temperature does not exceed 30 ° C. Avoid light.
SHELF LIFE: 24 months from date of manufacture
QUALITY STANDARD: Manufacture’s standard.
Made in
E’LOGE FRANCE VIETNAM JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Que Vo industrial zone, Phuong Lieu commune, Que Vo district, Bac Ninh province.
Tel: 0222.3617.888 Fax: 0222.3617.789